Diabetic Retinopathy:
Diabetic retinopathy (pronounced ret in OP uh thee) is a complication of diabetes that causes damage to the blood vessels of the retina—the light-sensitive tissue that lines the back part of the eye, allowing you to see fine detailz Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of irreversible blindness in working-age Americans. As many people with type 1 diabetes suffer blindness as those with the more common type 2 disease. Diabetic retinopathy develops in more than half of the people who develop diabetes.Causes:
The primary cause of diabetic retinopathy is diabetes— a condition in which the levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood are too high. Elevated sugar levels from diabetes can damage the small blood vessels that nourish the retina and may, in some cases, block them completely. When damaged blood vessels leak fluid into the retina it results in a condition known as diabetic macular edema which causes swelling in the center part of the eye (macula) that provides the sharp vision needed for reading and recognizing faces. Prolonged damage to the small blood vessels in the retina results in poor circulation to the retina and macula prompting the development of growth factors that cause new abnormal blood vessels (neovascularization) and scar tissue to grow on the surface of the retina. This stage of the disease is known as proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). New vessels may bleed into the middle of the eye, cause scar tissue formation, pull on the retina, cause retinal detachment, or may cause high pressure and pain if the blood vessels grow on the iris, clogging the drainage system of the eye— all of this can cause vision loss.WHAT IS THE RETINA?
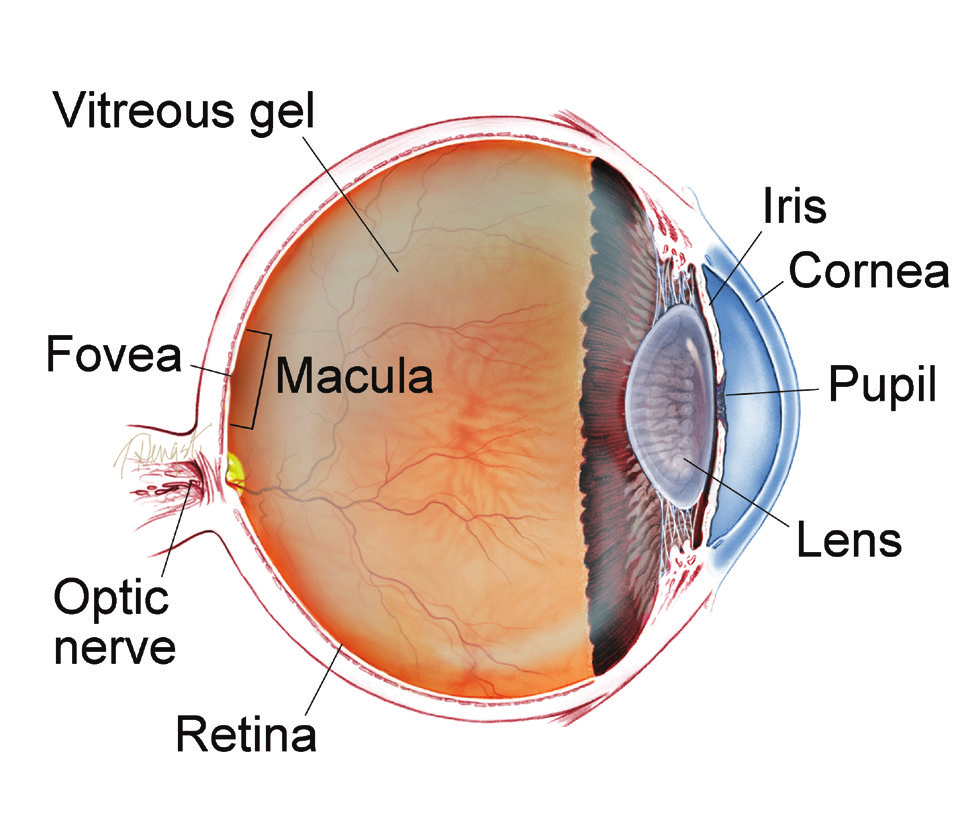
THE RETINA is a thin layer of light-sensitive nerve tissue that lines the back of the eye (or vitreous) cavity. When light enters the eye, it passes through the iris to the retina where images are focused and converted to electrical impulses that are carried by the optic nerve to the brain resulting in sight.
Risk Factors: Anyone who has diabetes is at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. Additional factors can increase the risk:
- Disease duration: the longer someone has diabetes, the greater the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- Poor control of blood sugar levels over time
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Pregnancy
SYMPTOMS
It is possible to have diabetic retinopathy for a long time without noticing symptoms until substantial damage has occurred. Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy may occur in one or both eyes.
Symptoms may include:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Difficulty reading
- Difficulty with color perception
- The appearance of spots—commonly called “floaters”—in your vision
- A shadow across the field of vision
Diagnostic Testing:
The best way to diagnose diabetic retinopathy is a dilated eye exam. During this exam, the physician places drops in the eyes to make the pupils dilate (open widely) to allow a better view of the inside of the eye, especially the retinal tissue. The physician will look for:- Swelling in the retina that threatens vision (diabetic macular edema)
- Evidence of poor retina blood vessel circulation (retinal ischemia— pronounced iss KEY me uh)
- Abnormal blood vessels that may predict an increased risk of developing new blood vessels
- New blood vessels or scar tissue on the surface of the retina (proliferative diabeticretinopathy) Regular dilated eye exams by an ophthalmologist are important, especially for those who are at a higher risk for diabetic retinopathy or diabetes. If you are over age 50, an exam every year is a good idea so the eye physician can look for signs of diabetes or diabetic retinopathy before any vision loss has occurred. In addition to checking for signs of diabetic eye disease, a comprehensive dilated eye exam will evaluate your vision/need for corrective lenses, eye pressure (looking for glaucoma), the “front” of the eye (eyelids, cornea, checking for dry eye), lens (looking for cataracts), as well as a complete exam of the retina and vitreous. In addition to this exam, physicians use other tests to detect and manage diabetic retinopathy:
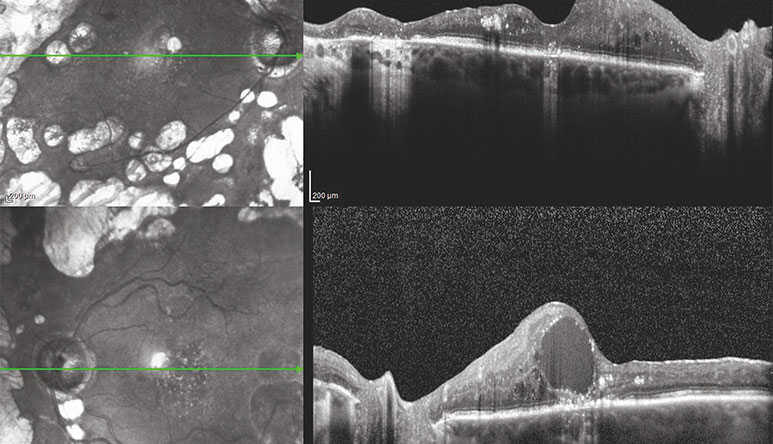
Figure 1
OCT of a patient with bilateral proliferative diabetic retinopathy with diabetic macular edema in the left eye. ©ASRS Retina Image Bank, May 2016. Image 26525. Olivia Rainey, Retina Specialists of Michigan.
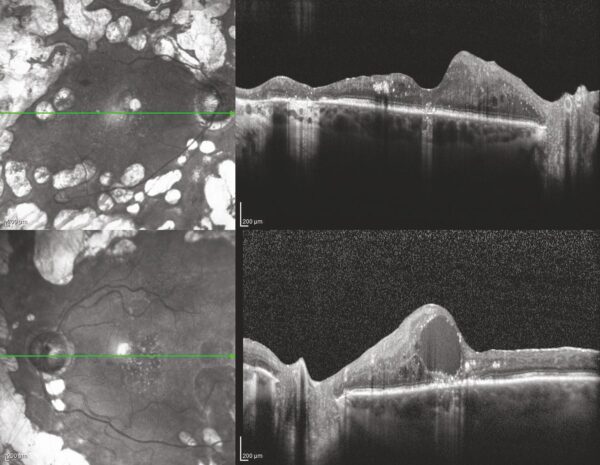
An optical coherence tomography (OCT) test provides highly detailed cross-sectional images of the retina that show its thickness, helping determine whether fluid has leaked into retinal tissue.
The physician may take fundus photographs of the back of the eye to help detect and document diabetic retinopathy. These photos make it easier for the physician to monitor the disease on follow-up visits to determine if it is worsening.
To evaluate retina blood vessel circulation, the physician may conduct a retinal photography test called fluorescein angiography (FA). After dilating the pupils, the physician will inject a dye into the patient’s arm. The dye then circulates through the eyes and works like a food coloring; however, it does not affect the kidneys and is unlike the dye that is used with MRIs and CAT scans.
As the dye circulates, the physician takes pictures of the retina to accurately detect blood vessels that are closed, damaged, or leaking fluid. The pictures are black and white to help the doctor detect these changes more easily, but the process does not expose you to any radiation. Prior to examination, ask your physician to discuss the risks and benefits of obtaining these images.
With proper examinations, diabetic retinopathy can be detected before vision loss begins. If the physician detects signs of diabetic retinopathy, she/he will determine how frequently follow-up examinations will be required to detect changes that would require treatment.
Figure 2
Retinal fundus photo of a patient with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. ©ASRS Retina Image Bank, 2012. Image 774. Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Duke University Hospital.
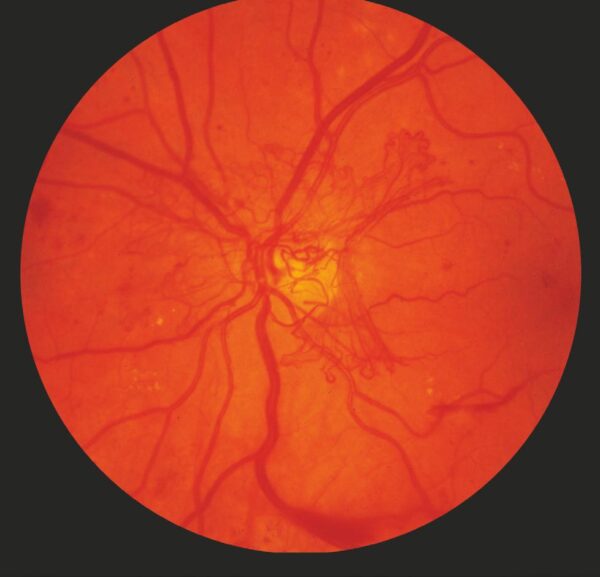
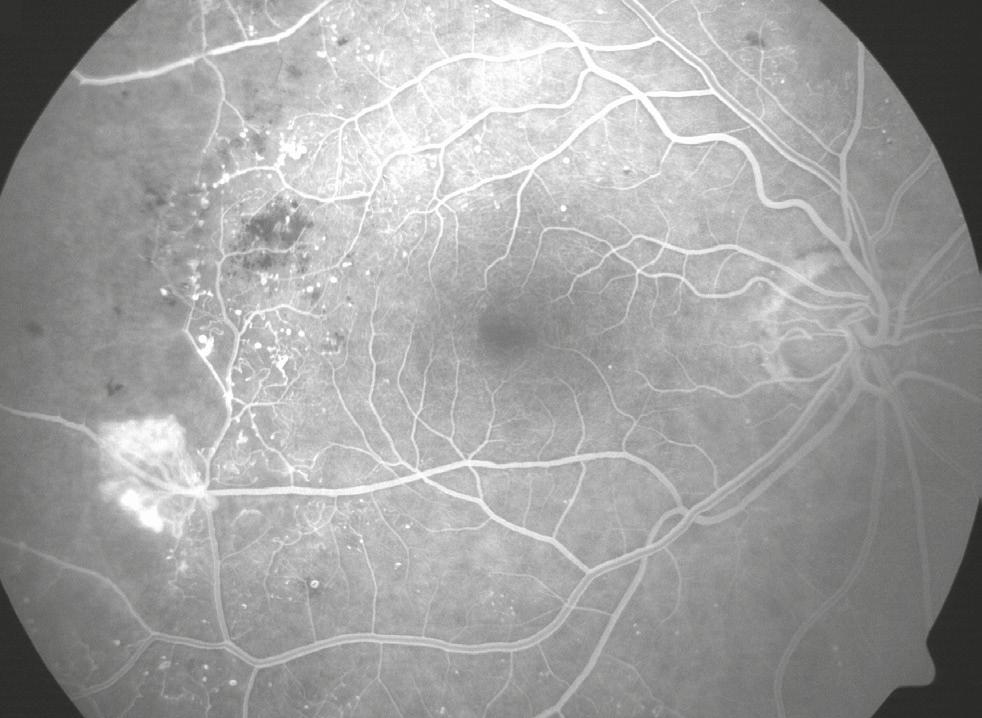
Figure 3
FA of a patient with proliferative diabetic retinopathy, retinal capillary nonperfusion, and neovascularization. ©ASRS Retina Image Bank, 2012. Image 2305. Sharon Fekrat, MD, FACS. Duke University Eye Center.
Treatment and Prognosis: As a result of major government- and industry-sponsored studies, there are many approved treatments for diabetic retinopathy, including intravitreal injections (small injections of medications into the middle cavity of the eye), laser treatments, and vitreous and retina surgery. These procedures can be done in an office or hospital setting to prevent, treat, or reverse damage from diabetes in the retina.
Research has shown that eye injections often result in better vision than laser treatment alone for patients with diabetic macular edema. The key to these treatments is their ability to block vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a chemical signal that stimulates leakage and abnormal blood vessel growth. Repeated doses of anti-VEGF medications may be needed to prevent blood vessels from leaking fluid and causing vision loss. Some eyes with diabetic macular edema respond better to intravitreal steroid injections than anti-VEGF injections. When proliferative diabetic retinopathy develops, this is treated with a laser treatment called panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) and possibly anti-VEGF injections. Vitrectomy surgery (removal of the vitreous) may be used in eyes with vitreous hemorrhage or severe scar tissue on the retina (epiretinal membrane or traction retinal detachment).
If you have been diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy or diabetes and have vision loss that cannot be reversed, a retina specialist can help you find access to rehabilitation with a variety of tools to make everyday living with this disease a little bit easier.
Prevention: Patients with diabetes frequently ask, “Is there anything I can do to keep from getting diabetic retinopathy or to prevent or treat vision loss once it occurs?”
If you have diabetes, the National Eye Institute suggests that you keep your health on TRACK:
- Take your medicines as prescribed by your doctor
- Reach and maintain a healthy weight
- Add physical activity to your day
- Control your ABCs—A1C, blood pressure, and cholesterol
- Kick the smoking habit
Regular dilated eye exams reduce the risk of developing more severe complications from the disease.
It is extremely important for diabetic patients to maintain the eye examination schedule put in place by the retina specialist. How often an examination is needed depends on the severity of your disease. Through early detection, the retina specialist can begin a treatment regimen to preserve your vision.
Diabetic macular edema (DME): The term used for swelling in the macula in eyes, or the center part of the retina which is responsible for providing the sharp, straight-ahead vision used for reading and recognizing faces as well as color vision.
Fluorescein angiography (FA): An imaging technique where a yellow dye called sodium fluorescein is injected into a vein in the arm. The dye allows a special camera to record circulation in the retina and choroid in the back of the eye. This test can be very useful in diagnosing a number of retinal disorders.
Fundus photography: Involves the use of specialized cameras equipped with lenses that capture images of the back of the eye where the retina, macula, vitreous, choroid and optic nerve are located.
Intravitreal injection: Treatment where a medication is injected into the vitreous cavity in the middle of the eye.
Macula: A small area at the center of the retina where light is sharply focused to produce the detailed color vision needed for tasks such as reading and driving.
Neovascularization: Excessive growth of new blood vessels on abnormal tissue as a result of oxygen deprivation that can cause vision loss.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT): A non-invasive imaging technique that uses light to create a 3-dimensional image of your eye for physician evaluation.
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR): An advanced stage of diabetic retinopathy in which new abnormal blood vessels and scar tissue form on the surface of the retina. The scar tissue can pull on the retina and cause retinal detachment and loss of vision. If blood vessels grow on the iris it can clog the drainage system of the eye causing glaucoma (high pressure in the eye), pain and vision loss.
Retinal detachment: A condition where the retina separates from the back of the eye cavity. This may be caused by vitreous gel or fluid leaking through a retinal tear or hole and collecting under the retina, causing it to separate from the tissue around it.
Bibliography
THANK YOU TO THE AUTHORS
Sophie J. Bakri, MD Audina Berrocal, MD
Thomas Ciulla, MD, MBA Geoffrey G. Emerson, MD, PhD Roger A. Goldberg, MD, MBA Dilraj Grewal, MD
Larry Halperin, MD Vi S. Hau, MD, PhD
G. Baker Hubbard, MD Talia R. Kaden, MD
M. Ali Khan, MD
Mathew J. MacCumber, MD, PhD Timothy G. Murray, MD, MBA Oded Ohana, MD, MBA Jonathan L. Prenner, MD
Carl D. Regillo, MD, FACS Naryan Sabherwal, MD Sherveen Salek, MD Andrew P. Schachat, MD Michael Seider, MD
Janet S. Sunness, MD Edward Uchiyama, MD Allen Z. Verne, MD Christina Y. Weng, MD, MBA Yoshihiro Yonekawa, MD
EDIT OR
John T. Thompson, MD
MEDICAL ILL US TRAT OR
Tim Hengst
Copyright © The Foundation American Society of Retina Specialists
Committed to improving the quality of life of all people with retinal disease.
Search
Recent Posts
-
 Understanding Vitreoretinal Surgery: Comprehensive Eye Care at Nishant Taneja
24-Nov-2025
Understanding Vitreoretinal Surgery: Comprehensive Eye Care at Nishant Taneja
24-Nov-2025
-
 Trabeculectomy: A Key Solution for Glaucoma Management
24-Nov-2025
Trabeculectomy: A Key Solution for Glaucoma Management
24-Nov-2025
-
 Enhance Your Eye Health and Appearance with Oculoplasty Surgery at Nishant Taneja Eye Clinic in Tirana
29-Jul-2024
Enhance Your Eye Health and Appearance with Oculoplasty Surgery at Nishant Taneja Eye Clinic in Tirana
29-Jul-2024
-
 Correcting Eye Misalignment with Strabismus Surgery at Nishant Taneja Indian Eye Institute & Laser Center
29-Jul-2024
Correcting Eye Misalignment with Strabismus Surgery at Nishant Taneja Indian Eye Institute & Laser Center
29-Jul-2024
-
 Say Goodbye to Glasses! Glasses Removal at Nishant Taneja Indian Eye Institute & Laser Center
29-Jul-2024
Say Goodbye to Glasses! Glasses Removal at Nishant Taneja Indian Eye Institute & Laser Center
29-Jul-2024