SMILE PRO Technology
SMILE is the most recent and advanced form of laser assisted refractive surgery. SMILE stands for Small Incision Lenticule Extraction and is creating a revolution in the realm of laser vision correction procedures like never before.
SMILE is the first ‘NO FLAP’ technique that makes a small 2mm cut in the cornea to remove a thin slice of corneal tissue, unlike LASIK that creates a flap by cutting 28mm circumference of cornea. It uses a single femtosecond laser throughout the procedure, unlike LASIK that employs an excimer laser to treat the cornea under the flap. Here the tissue damage especially to the corneal nerve fibers is almost nil as compared to other laser-based procedures.
Now available at Indian Eye Institute and Laser Center in Albania, this revolutionary laser procedure redefines vision correction. The actual laser procedure in SMILE Pro lasts just a few seconds, and hence, SMILE Pro is a smarter, safer, and faster way to enhance the quality of life while giving freedom from eyeglasses.
Indian Eye Institute and Laser Center is the first and only eye hospital in Albania to offer SMILE pro laser treatments for individuals seeking the most advanced & safe laser vision correction.
Top features of SMILE Pro technology:
SMILE Pro represents the next generation in vision correction, catering to individuals looking for instant, painless, and safe laser vision corrections.
- Near Non-Invasive: In contrast to LASIK, which creates a flap, SMILE needs an incision of 2-3 mm to extract a lenticule for vision correction. The small incision and the precision of the femtosecond laser in SMILE results in excellent corneal biomechanical stability.
- Flapless procedure: SMILE Pro technology is American FDA-approved known for its accuracy, fastervision recovery, and painless features. Unlike traditional LASIK, SMILE Pro involves a single-step, flapless procedure and hence there is no chance of the flap moving or folding.
- NO Blade: SMILE is an all-laser procedure that involves no use of any blade or needles.
- Faster Recovery: With SMILE, Patients recuperate more quickly and have less downtime.
- Improved Comfort: SMILE Pro reduces the occurrence of dry eyes and other complications. As corneal nerves are untouched in SMILE the incidence of dry eye is almost nullified resulting in better patient comfort following SMILE.
- Long-Lasting Results: Offers consistent and dependable visual results
- Fastest procedure: SMILE pro takes less than 10 seconds for actual vision correction.
- The procedure is also not affected by external factors like temperature and humidity as there is no flap which results in higher treatment accuracy. With SMILE the disadvantages of older laser vision correction treatments are eliminated retaining their advantages.
SMILE Pro with Albania’ s best and only SMILE pro surgeon, Dr Nishant Taneja
This hospital combines the best technology with the best surgeon.
Indian Eye Institute and Laser Center is the only centre that offers SMILE Pro technology.
Dr Nishant Taneja ranks among the best eye surgeons with 20 years of experience. Dr. Taneja has transformed countless lives with his surgical expertise and niche skills.
The bladeless, minimally invasive SMILE Pro treatment corrects myopia , hypermetropia and astigmatism with unrivalled accuracy and safety.
This innovative method reshapes the cornea with a single, microscopic incision, resulting in speedier recuperation, reduced dry eye concerns, and excellent vision.
Refractive errors of the eye
Refractive error represents an optical imperfection of the eye, i.e. the inability of the eye to sharpen the image. You are short-sighted (myopia) if you see clearly the objects in close proximity, while the distance is blurred (for example, you do not recognize a person coming towards you, you can not drive without glasses or watch TV). In this case the image focuses in front of the retina (inner coat of the eye sensitive to light stimuli) and you need negative diopter value in order for the image to focus directly on the retina and to be sharp.
You are far-sighted (hyperopia) if you do not see clearly distant nor close objects (for example, you do not recognize a person coming towards you, you cannot drive without glasses or watch TV, but you also have blurred vision when reading, working on a computer, writing messages on your phone – your eyes strain or you have headaches working at short distance). In this case the image focuses behind the retina and you need positive diopter value in order for the image to focus directly on the retina and to be sharp.
You have astigmatism if both close and distant objects are blurred and have a shadow. Astigmatism refers to an irregular curvature of the cornea.
Fast, safe and painless path to perfect vision
Laser vision correction refers to procedures performed by laser cornea remodeling (transparent front part of the eye) with the purpose of removing or decreasing the diopter value, eliminating optical aids and improving visual acuity. Today there are several methods of vision correction, and the basic division is based on the depth of the cornea at which the operation is performed (the surface of the cornea -PRK, LASEK and middle of the cornea – LASIK).
Nowadays all types of operations are fully computer-controlled by precise software programs. Modern lasers can remove one diopter value in less than 2 seconds. Systems used for tracking the eye of a patient during the operation (tracker) allow a precise delivery of the laser beam to an exact place regardless of the micromovements of the patient’s eye during the laser procedure. Because of the perfect precision and fast software systems all of the procedures performed today are 99% safe. The selection of the method nowadays depends solely on the characteristics of the eye, the value of the diopter and the lifestyle of the patient.
Modern lasers can correct diopter values from -10.0 to +6.0 as well as ±5.0 astigmatism diopter value, which means that almost 95% of people are candidates for Laser vision correction surgery. People with diopter values higher than those stated above, also have a solution for vision correction by implantation of the most sophisticated lenses into the eyes with equally good results, and in some cases even better results than laser vision correction.
What is FemtoLASIK Eye Laser Treatment?
Femto-LASIK is an advanced form of LASIK eye surgery designed to correct refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), astigmatism (irregular curvature of the cornea), and presbyopia (age-related farsightedness). The main difference from traditional LASIK is that Femto-LASIK uses a femtosecond laser instead of a mechanical microkeratome (a surgical instrument) to create a thin corneal flap. This process is highly precise and minimizes the risk of complications during the flap cut.

After the flap is created, it is gently lifted to expose the underlying corneal tissue. A second laser, the excimer laser, is then used to precisely reshape the cornea, correcting the refractive error. After reshaping, the flap is repositioned, where it heals without stitches.
The advantages of Femto-LASIK over traditional LASIK include higher precision in flap creation, reduced likelihood of flap-related complications, potentially faster healing, and improved safety. Because the femtosecond laser enhances control and accuracy of the procedure, Femto-LASIK may also be suitable for patients who are not candidates for traditional LASIK due to thin corneas or other factors.
LASIK vs. Femto-LASIK: What’s the Difference?
Both LASIK (Laser-Assisted In-Situ Keratomileusis) and Femto-LASIK are procedures for correcting vision problems like myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism, but they differ in the technology and method used to create the corneal flap.

LASIK
- Uses a microkeratome, a precise surgical instrument with a fine blade, to create a thin flap in the outer layer of the cornea.
- After the flap is created and folded back, a highly precise excimer laser, such as the Mel 90 from Zeiss, reshapes the underlying corneal layer to correct the refractive error.
- The flap is then repositioned, where it heals without stitches.
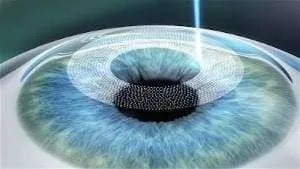
FemtoLASIK
- Also known as “bladeless LASIK” or “all-laser LASIK,” uses a femtosecond laser instead of a microkeratome to create the corneal flap.
- This laser produces extremely short and fast light pulses that form precise microbubbles beneath the surface of the cornea, creating a flap without mechanical cuts.
- Like LASIK, the flap is folded back, and an excimer laser is used to reshape the cornea to correct the refractive error. The flap is then repositioned to heal naturally.
Main Differences:
- Technology: Femto-LASIK uses a femtosecond laser for flap creation, while LASIK uses a microkeratome (mechanical blade).
- Precision and Safety: Femto-LASIK is considered more precise and safer for flap creation, as laser creation involves fewer risks than mechanical cuts.
- Healing Process and Outcomes: Both methods offer similar results in terms of vision improvement, but some doctors and patients prefer Femto-LASIK due to its higher precision and potentially lower complication rate.
The Safe and Proven Eye Laser Treatment
In bladeless LASIK—also known as bladeless LASIK, all-laser LASIK, or Femto-LASIK—your LASIK surgeon uses two types of lasers for vision correction.
First, an ultra-fast femtosecond laser creates a thin flap in the cornea (the clear front surface of the eye). Then, an excimer laser reshapes the underlying corneal tissue to correct your vision. Then, the flap is repositioned to its original position, and the side of the flap is absorbed with a sterile sponge to create initial adhesion
The Femto-LASIK procedure is a modern and gentle method to correct refractive errors. By using state-of-the-art technology and the extensive experience of our doctors, we offer our patients particularly precise and safe treatment.
In Femto-LASIK, a special laser first creates a flap in the upper layer of the cornea. This flap is a very thin and even disc of corneal tissue that sits like a lid on the cornea. This flap provides access to the underlying corneal tissue, which can be reshaped with the excimer laser to correct refractive errors such as myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism.
The advantage of the flap is that it acts like a natural protective shield on the cornea, enabling faster and less disturbed healing. The flap is gently repositioned after the correction and adheres to the cornea on its own.
Femto-LASIK with thin flaps uses a fully computer-controlled femtosecond laser system to precisely and safely create ultra-thin flaps in the first step of the LASIK procedure.
The femtosecond laser eliminates the need for a surgical instrument with blades (a so-called microkeratome) to create the corneal flap. In all-laser LASIK, no surgical blade is required.
Requirements for Femto-LASIK
The suitability for a FemtoLASIK operation corresponds precisely to the suitability for other types of laser eye surgery.
In summary:
- Minimum age: 18 years
- Not pregnant or breastfeeding
- No serious eye diseases
- Adequate corneal thickness
- No significant change in refractive error in the past two years
Application Range of Femto-LASIK
- Mild/moderate myopia, hyperopia, and/or astigmatism, adequate corneal thickness
- Myopia: up to -10.00 D
- Hyperopia: up to +4 D
- Astigmatism: up to 5 D
Before the Operation:
- Perform all necessary examinations for treatment, including an extensive pre-examination.
- Do not wear contact lenses for 14 days before the examination appointment.
- Pupil dilation on the day of the pre-examination, no driving possible afterward.
The Operation:
During the operation, you will not feel any pain and will be guided by your surgeon.
- Numb the cornea with drops for a painless eye laser procedure.
- Personalized treatment with iris recognition to set the laser for each eye.
- The excimer laser performs the individual correction of the refractive error for each eye, using data from the computer-assisted wavefront analysis.
- Create a corneal flap. During this process, vision may be darkened for a few seconds.
- The laser gently reshapes the inner corneal layer to correct the refractive error. An eye-tracking device monitors eye movements to ensure precise correction.
- Reposition the flap to its original position.
After the Operation:
- After treatment, the patient receives sunglasses to avoid friction, artificial tears, and some sleeping pills, as the flap is sensitive for a few hours.
- Keep eyes closed and sleep for 4-6 hours after the operation. The natural position of the eyelids helps the corneal flap to adhere gently and permanently to its original position in the eye.
- Spend the rest of the day quietly without strenuous activities.
- Due to pupil dilation, no driving is possible.
The Next Day
- Follow-up examination at the LasikWelt Eye Laser Center.
- Usually, you can drive again after this appointment.
The Advantages of Femto-LASIK Over Traditional LASIK
Femto-LASIK not only offers the advantage of patient comfort (knowing that no blade is used on the eye) but also:
- More predictable corneal flap thickness
- Lower risk of corneal abrasions during the procedure
- Fewer flap-related complications
- Reduced risk of induced astigmatism post-LASIK
- In some cases, a femtosecond laser can also allow for the creation of a thinner corneal flap, enabling the surgeon to safely correct higher myopia.
- Femto-LASIK is safer than PRK, as evidenced by a study in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.
- Additionally, the femtosecond laser provides the LASIK surgeon with more options in terms of flap size, shape, and orientation, allowing the procedure to be better tailored to the individual needs of each patient.
- Patient satisfaction after a Femto-LASIK treatment is very high, as shown by a study in Clinical Ophthalmology (source: PMC).
- Lastly, the femtosecond laser can create a corneal flap with edges that ensure the flap sits more securely after the LASIK procedure, reducing healing time and the risk of flap displacement post-operation.
Possible LASIK Complications
LASIK treatments are highly effective, with most patients achieving excellent vision correction. However, like any medical procedure, there is a small risk of complications, which can be short-term or long-term. In rare cases, problems can even be permanent.
However, you shouldn’t worry, as LASIK complications are very rare. According to the Eye Surgery Education Council (ESEC), established by members of the American Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery (ASCRS), less than 1% of LASIK patients experience serious problems (source: Eyeworld). This demonstrates that LASIK treatments are generally very safe.
FemtoLASIK is proven to be a safe and effective procedure for vision correction. Flap complications—mostly associated with traditional LASIK using a microkeratome blade but rarely also with FemtoLASIK—can occur in very small numbers. Some possible complications include eye infections, chronic dry eyes, and issues with the LASIK flap. Fortunately, most of these complications can be treated and heal within a few months.
Furthermore, studies show that LASIK complications decrease with the experience of the doctors, and technology is continually advancing.
Ultimately, the risk of complications also depends on your overall health. Patients with certain conditions, such as diabetes, may have a higher risk of complications. Therefore, it is important to inform our specialists about your health condition and ask any questions you may have. It is also important to note that each patient responds differently to the treatment, and the healing process can vary for each individual
LASIK Method

Allegretto Wavelight Excimer Lazer
LASIK
LASIK (Laser in Situ Keratomileusis) is the most commonly performed type of surgery for vision correction. LASIK is the most common choice of surgeons due to its high accuracy, excellent and long-term stable postoperative results, the complete absence of pain (both during the surgery and in the postoperative period) and a very rare occurrence of complications.
LASIK procedure is a two-step operation. The first step is the forming of the flap (flap on the cornea), and the second is the remodeling of corneal surface using excimer laser. The flap on the cornea can be formed in two ways:
- With mechanical microkeratome (knife, LASIK with microkeratome)
- With femtosecond laser
Femtosecond LASIK

Femto – LASIK (Synonyms: ALL – Laser LASIK, Bladeless LASIK, iLASIK, Z-LASIK).
Indications for surgery are diopter values from -10.0 to +6.0, and up to ± 5.0 cylinders of astigmatism. This type of LASIK method is fully automated and laser-controlled, without using the knife blade. Femtosecond lasers have been in use since 2001 and they have primarily presented a new step forward in the safety of LASIK surgery. Today, the surgeries in our Hospital are performed exclusively on IntraLase , IFS 150 Hz femtosecond laser, which is also the latest generation and the most commonly used femtosecond laser in the world.
Due to the precision of the incision, the flaps of the cornea (the lids on the cornea) have a more regular shape and more predictable thickness compared to flaps made by microkeratome. Therefore, the advantage of such method is of particular importance in higher diopter values, astigmatism and thinner corneas It also reduces the possibility of occurrence of dry eye and enables better healing.
LASIK with microkeratome (standard LASIK)
This is the first developed LASIK method which, besides good technology, also needs an experienced hand of a surgeon to form the flap (the lenticule on the cornea) with the help of microkeratome. Microkeratome is an automated electric knife used for the forming of the flap on the cornea. In the last 25 years the quality, speed, precision and efficiency of mechanical microkeratome has been constantly improving, which led to a significant increase in safety and precision of the surgery. Last generations of microkeratome that we use in our clinic allow very precise forming of flap on the cornea, regular edges and predetermined thickness and shape. The procedure lasts only a few minutes and does not create any discomfort to the patient.
PRK method (Photorefractive keratectomy)
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) is the oldest laser procedure for the remodeling of the cornea which has undergone a series of improvements over the years. The remodeling of the cornea with an excimer laser in PRK method is performed on the corneal surface after removing the epithelium (the renewable superficial layer of the cornea).
The operation is suitable for people with negative diopter values, with astigmatism up to 3.0 diopters, in mild irregularities of the cornea, in cases of a thin cornea and corneal scars.
PRK is the oldest method of laser vision correction. It was performed for the first time in 1987. The method involves mechanical removal of the epithelium (the renewable superficial layer of the cornea) and then remodeling of the cornea with an excimer laser. The epithelium is usually removed with a knife. After the treatment a “wound” is left on the eye which needs 4-7 days to heal. The surgery itself is not painful, but the postoperative recovery in case of this method can be uncomfortable. Generally, the recovery of visual acuity depends on the epithelial healing. Complete stabilization of vision quality often takes up to several weeks.
Other vision correction methods: phakic lenses implantation
People with extremely high diopter values (over -10.0 or +6.00) or corneas (transparent front part of the eye) that too thin or irregular (diagnosed during examination) and because of it laser vision correction would expose them to the risk of complications have an option of phakic lens implantation (Implantable Collamer Lens-ICL, or iris claw- Artisan, Artiflex) into the eyes.
Phakic lenses are implanted into the anterior eye segment (in front of or behind the pupil), without removing the natural lens and they function as a contact lens in the eye but the patient does not feel them and does not have to take care of them.
The operation is performed through small incisions which usually do not even need to be sutured. Surgery is almost completely free of complications and extremely harmless for all structures of the eye (no structure of the eye is removed). It is especially suitable for young people (between 20 and 50 years) who still have the possibility of eye accommodation, i.e. the adjustment of image focus both at distance and at proximity. Also, the procedure is reversible, i.e. the lens can be removed from the eye (the eye returns to its preexisting diopter) without additional damages (in case of an increase in diopter and the need for implantation of more powerful lenses or the arrival of new significantly better and more advanced technologies).
There are several types of these lenses (Implantable Collamer lens- ICL, or iris claw- Artisan, Artiflex) which enable the treatment of diopter value range from -23 to +21 diopter as well as 6 cylinder of astigmatism.
Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL)
Lenses are implanted behind the pupil (in the posterior eye chamber between the iris and the natural lens). At the moment, they are considered the best solution for people who are not suitable candidates for laser vision correction, and have a diopter range from -0,5 to -18.0 and from +0.50 to +8.0 they also correct astigmatism up to 6.0 diopter. Compared to other generations of phakic lenses, they have better optics and are more suitable for people with a large pupil diameter. Also, due to lens position inside the eye, it has been observed that in patients with a large negative diopters it significantly improves visual acuity compared to glasses and contact lenses. It is made of biocompatible material and it does not cause immunological eye reaction, and it also has anti-reflective and UV protective properties.
Artisan / Artiflex
Lenses are implanted in front of the pupil onto the iris. They give excellent quality of vision for people with high diopters, and are now being implanted in cases where diopter value is greater than the diopter range of ICL phakic intraocular lenses as well as in people with a weak supporting eye apparatus which is unable to keep the lens behind the pupil. Lenses exist on the market for more than 30 years and have on their side the greatest world experience which indicates excellent results and procedure stability.
Specialized therapeutic methods
Laser vision correction - the treatment of scars and higher order aberrations
In addition to vision correction, laser technology is also used to treat parts of the scars and corneal dystrophy. The most common method for treating these kinds of diseases is PTK (phototherapeutic keratectomy) which remodels the surface of the cornea (transparent front part of the eye) in order to remove part of the blur and reduce irregularities that decrease quality of vision. After the procedure, medications like mitomycin are often used. Those medications further enhance the clearing of cornea and control healing in order to maintain the desired result.
Examination
Examination for laser vision correction
The examination for laser vision correction is a very detailed examination of all parts of the eye. To implement this procedure, the eye needs to be healthy, i.e. any irregularities, diseases or conditions must be either cured or well controlled before laser vision correction is performed.
The examination for the laser vision correction begins with assessment of corneal topography (imaging of the anterior transparent part of the eye) in order to gain insight into corneal curvature and thickness. After corneal imaging, assessment of whole eye high order aberrations is performed. Those tests are performed to detect any irregularities, other than diopter, which could potentially decrease the performances of the eye as an optical apparatus. After those tests, patient’s visual acuity is checked.
After above mentioned examinations, the pupils are dilated for the purpose of additional objective assessment of the diopter (the dilation of the pupil excludes muscle action, or the so-called accommodation that may show a false high or low diopter in some patients).
Also as part of the examination intraocular pressure is measured, tear film evaluated, and detailed examination of posterior part of the eye (retina) is performed. Fundoscopic examination includes an examination of the optic nerve, the macula (center of sight), and the periphery of the retina, which is often thinned in people with high diopters.
In case of finding any irregularities, we perform more tests depending on the finding.
Duration of the examination is usually between 90 and 120 minutes. Patients who wear contact lenses must discontinue their usage before the examination (contact lenses can change corneal surface and influence measurements). For soft contact lenses this should be done three days before the examination and for (semi) rigid contact lenses eight full days before the examination. Due to the dilation of the pupils, the vision may be slightly blurred for a short period after the examination.
Am I a candidate for laser vision correction?
95% of persons older than 18 years of age with a diopter being stable for a year (changes in the diopter less than 0.50D) can undergo laser vision correction. The laser can correct the diopter from -10.0 to +6.0 and up to ± 6.0 cylinders of astigmatism.
Laser vision correction can correct myopia (shortsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness) and astigmatism so that the patient will not have to be dependent on glasses or contact lenses.
Glasses can be a nuisance for people who have active lifestyles, especially during sports activities. They wear contact lenses as an alternative.
Although contact lenses provide good vision for many people, they do have limitations such as a dry eye, eye allergies and eye infections. If you wear them for a longer period, contact lenses cause damage to the eye due to a lack of oxygen and can lead to the infection of the cornea that can be very serious. With these limitations, the solution method is LASIK.
The candidates for LASIK should:
- Be more than 18 years of age
- Have a stable diopter for at least a year
- Have a diopter in the range from -10.0 to +6.0 to ± 6.0 cylinders of astigmatism
- Have a healthy cornea
The procedure and recovery
Surgery and Recovery
Laser vision correction is a completely painless procedure performed under topical (eye drop) anesthesia. Procedure is performed as an outpatient treatment and the patient can be discharged half an hour after the procedure.
Laser vision correction lasts 5-10 minutes per eye, depending on the method. It is performed under topica (eye drop) anesthesia and is completely painless. The eye is kept open during the surgery with the help of a special eyelid holder which enables the patient to blink. The patient is awake during the entire surgery and is usually instructed to look toward the fixating green lights.
Modern lasers are equipped with eye trackers in several dimensions so that accidental movements of the patient’s body and eye do not affect the safety and precision of the procedure.
Postoperative recovery
Postoperative recovery depends on the vision correction method. After the procedure with LASIK the patients can return to most of their regular activities in a couple of days, while after PRK they need to wait five to seven days.
Postoperative recovery usually depends on the method of vision correction. The first day after the surgery the image is usually blurry (as if seen through water), but there is a significant clarification of the image already the next day. The fastest vision recovery is with LASIK, while with PRK method complete recovery is slower and depends on the speed of healing of the eye surface. With both methods it is extremely important to avoid eye contact with any potentially unclean surface (fingers, tap water) for several days.
With LASIK, it is not recommended to wash the eyes with tap water 3-4 days, while with PRK it is not recommended until the healing of the surface of the eye and the removal of therapeutic contact lenses. Within a week of surgery, it is possible to return to all daily activities. Because of the danger of contamination, infection and irritation, it is recommended to avoid swimming in the sea for 10 days, and in the pools for at least three weeks.
Moderate sports activities are allowed after 5-6 days, but team ball sports and martial arts should be avoided for at least a month due to the risk of accidental injury. Also, lifting of heavy loads is not recommended for a month.
After all the procedures, it is necessary to instill drops in combination with an antibiotic/ corticosteroid for two weeks and artificial tears for at least a month.
Diagnostics and technology
Diagnostic devices
Corneal topographers
OCULUS Pentacam HR and CSO corneal topographers take images of the corneal surface and are the most important examination when selecting candidates for laser vision correction. The apparatuses take images of the front and back surface of the cornea. They show in digital form the actual corneal surface, as well as the mathematical models that indicate the existence / non-existence of deviations from a perfectly healthy eye. In addition to imaging the corneal surface, both topographers automatically map the higher order aberrations of the cornea and present and analyze the image of the entire anterior ocular segment (anterior chamber, pupil, iris, lens thickness).

Pentacam HR is considered the gold standard (reference device) in the topography of the cornea and it can make 100 images of the cornea in a second, with 138 000 processed points in only 2 seconds.
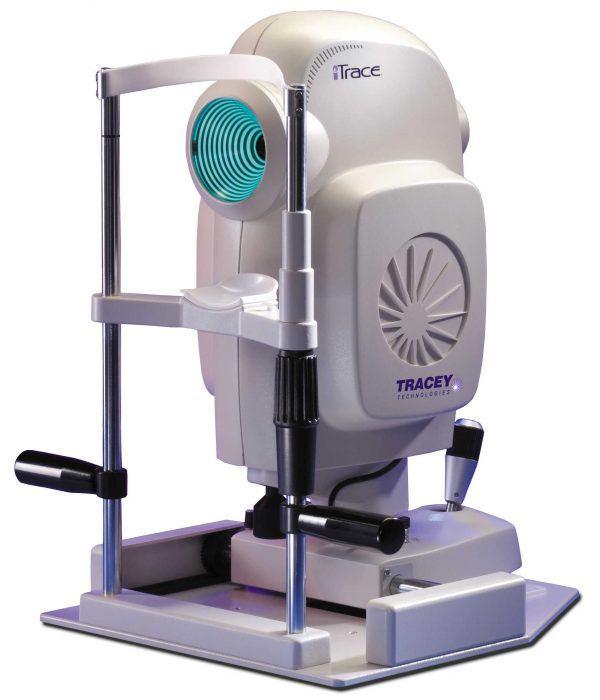
Tracey - iTrace Aberrometer
Aberrometers
Tracey – iTrace aberrometer map lower order(the diopter) and higher order aberrations of the entire eye. The data on the aberrations is obtained from the analysis of over 1500 points. Objective data on the diopter completely eliminate the possibility of erroneous correction and reduce the need for the patient to decide on the best image quality (the exact diopter). Laser correction of higher order aberrations primarily improves the quality of night vision (light scattering is reduced). CSO IRX aberrometer is directly linked to the excimer laser and allows the use of personalized treatments.
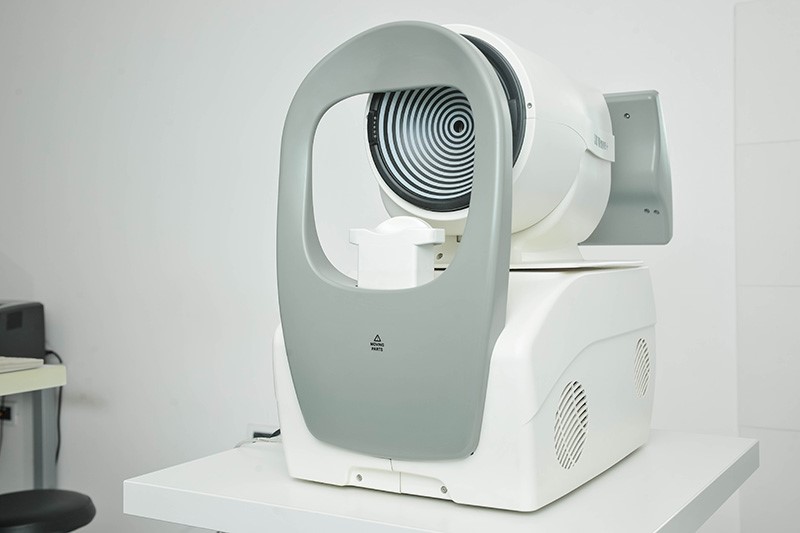
Pupilometer
CSO pupilometer measures the size of the pupil in all lighting conditions by changing the lighting conditions during imaging. The data on the maximum diameter of the pupil (the pupil at night) is essential for the planning of laser surgery. Excimer laser ablation zone (part of the cornea where diopter is corrected) has to be wider than the widest pupil in order to prevent night vision disturbances.(halo, glare)
Method of examination
The patient sits on the device, lays his head and the device automatically captures the cornea with the corneal topographer, or aberrometric profile of the eye with the aberrometer. The examination is painless, the imaging takes a few seconds. The test is not harmful, and the finding is immediately obtained in a digital form or printed on the printer.
Laser technology
Wavelight Allegretto 400Hz
(Alcon Laboratories, USA) – Allegretto is the second fastest laser in the market that operates at a speed of 400 Hz and takes about 2 seconds to remove one diopter. Equipped with twice as fast eye monitoring system so that it delivers a safe and accurate result in the case of moving of the patient’s eye. Allegretto is the most commonly used laser in Europe with excellent and stable results.

AMO Intralase 150Hz
(Abbott Medical Optics, USA) is a femtosecond laser for flap creation. It is currently the most commonly used femtosecond laser on the market with very positive experiences by users in the last 10 years (it operated on over several million eyes at the global level, while all other lasers have operated merely on thousands).
The laser is characterized by extremely low level of complications that leave no consequence to the eye and vision and are correctable in the same surgical procedure. The laser offers the possibility of adjusting the shape and size of the flap to each individual diopter and the eye and the possibility of changing the angle of entry which increases postoperative corneal strength. It almost completely prevents subsequent flap movements in cases of serious eye damage.