We at Indian Eye Institute and Laser Center carry out surgeries for all types of strabismus (horizontal, vertical, palsy, nystagmus, double vision). We also perform strabismus surgeries on adults and the surgery of opening and irrigating the tear duct in children under a short-term general anesthesia. We use the same methods and surgical techniques used in the world’s best centers.
Children's examination
Children’s eye examination lasts two hours and includes:
- Assessment of visual acuity at near and far distance
- tests for strabismus and stereopsis
- dilatation of pupils and assessment of objective diopter
- full examination of the anterior and posterior ocular segment.
Methods for assessing visual acuity are different depending on the age of the patient. When assessing baby’s special cards with patterns are used with which one can determine what size of the sample raises the baby’s attention and the result is compared with the expected results prescribed for a certain age.

For preschool children little symbols (Lea symbols) are used which are regulated by the same geometrical progression as characters for adults. In order to get more accurate resultsit is necessary to examine the child’s ability to recognize the little symbols at near and far distance. The same tables of letters are used for school-age children and adults.
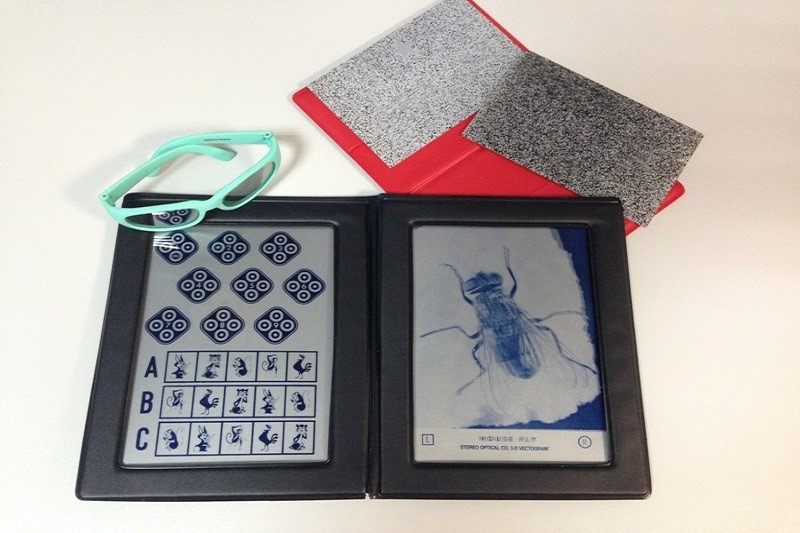
Taking the orthoptic status (examination for strabismus) is also a necessary part of the child’s examination, and is necessarily performed for adults who have strabismus. It serves to assess thepresent situation and adequate mobility as well as cooperation between both eyes. In this partof the examination, we measure the deviation angle, determine the type of strabismus and disorders of binocular vision (whether the child has the ability to use both eyes together while watching), amblyopia (lazy eye), and nystagmus (wobbly eyes). The development of stereopsis (3D vision) is established using stereo tests (Titmus test, Lang test). In children or adults who have nystagmus (wobbly eyes) in this part of the examination additional measurements are carried out.
The procedure of assessingthe objective refractionof the child is somewhat different than in adults because of strong adaptability (accommodation) of the children’s eye that sometimes easily conceals even greater diopters. To exclude this adjustment, it is necessary to widen the pupil, which is achieved by putting in eyedropsseveral times, and the entire procedure takes about an hour. It is advisable to prepare children at home for the fact that drops will be putinto their eyes and that they will have a blurry visionafter the examination (lasting for a few hours to a full day). After the pupils have fully dilatedthe objective assessmentof the diopter is done – retinoscopy, extremely important for assessingpossible hidden diopters or other visual disturbances. Althoughthe cooperation of the child is necessary to determine visual acuity, objective diopter can be determined even for the smallest child because it does not require itscooperation.
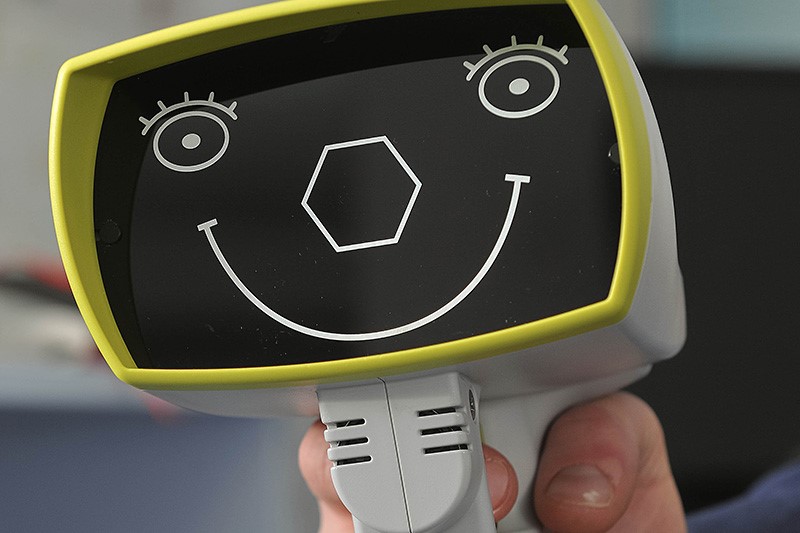
To assessthe objective diopters in children we use specially adapted children’s refractometer Plusoptix.

The anterior eyesegment is examined on a split lamp with a microscope to rule out signs of inflammation, allergies and any anatomical abnormalities. The examination of the the posterior eyesegment (retina) is done in order to thoroughly examine the eye.
Examination for strabismus
The examination for strabismus includes full eye examination consisting of the assessment of visual acuity, determination of the diopter on automatic computer refractometer, eye pressure check(measurement of intraocular pressure ), anterior eyesegment examination on a slit-lamp, tear film assessment (Schirmer test), then the pupils are widened to examine the optic nerve and retina and establish the objective diopter.
Examination for strabismus includes establishingthe orthoptic status. Examination has to be done for children and the patients with strabismus. Performingthe orthoptic status is used to check the position and adequate mobility as well as cooperation between both eyes. In this part, the type of strabismus is determinedand the the deviation angleis measured. Angle of squinting is measured by prisms in the prism diopters (PD). It needs to be measured at near and far distance and in all gaze directions.

The mobility of the eye is checked for each eye separately (duction) as well as coordinated movement of both eyes (versions and vergencies). The following step is assessing the degree of binocular vision (proper cooperation of both eyes with creating a stereo image – Bagolini test, Titmus test, Lang test).

When necessary, testing for double vision is performed. The measurement of accommodation (adjustment of the eyes for near vision) is also conducted when the strabismus surgery is required, simulation and check of the planned eye position is simulated before the planned surgery
Surgery and recovery
Surgeries on children’s eyes are performed under general anesthesia. A child should arrive for surgery after the recommended period without eating and drinking with laboratory tests that are necessary for general anesthesia. Before the procedure, the anesthesiologist talks to the parents about the general health of the child, history of other diseases and goes through laboratory results. Only after being examined by an anesthesiologist, the child is ready for the procedure.
Can parents accompany child during hospital postoperative recovery?
After surgery, a parent stays with the child in a hospital room. Depending on the type of surgery,the child remains in the clinic until next day, or can leave in few hours, in both cases a parent stays with thechild.
How does postoperative care of childlook like?
In the most cases after the surgery, the child have to wear a bandage over the operated eye. The parents should pay special attention that the child does not remove the bandage or rub the eye.. During recovery, the child needs to put eye drops in the operated eye for a recommended period of time depending of the type of the surgery.. The parents should take special care that the prescribed therapy is applied directly in the eye.
How frequent are follow-up visits after the surgery?
The first follow-up is usually scheduled the day after the surgery, and following visits depend on the type of surgery. Usually they are performed in intervals of one to two weeks after surgery.
Diagnosis and technology
Pediatric binocular autorefractor Plusoptix
Pediatric binocular autorefractorPlusoptix is indispensable device for determining the refractive status of the eye. It is specially designed and adapted for small children and babies. It can also be applied in patients with special needs. Plusoptixworks on the principle of simultaneous binocular diopter measurement at a distance of one meter. Other than diopter, it measures the size of pupil, pupillary distance and corneal reflex. The taking of measurement is very simple, a child has to look into the camera for for only 0.8 seconds, at the same time the machine lights up and produces sounds that attract child’s attention.

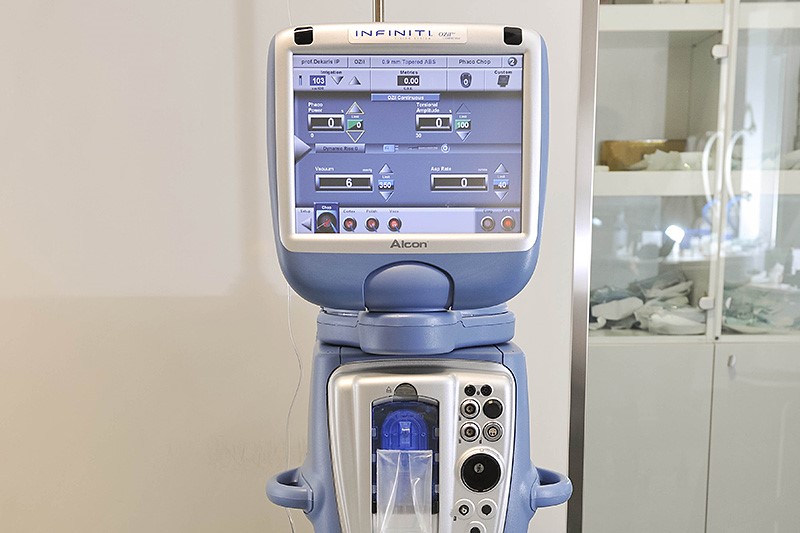
Equipment for cataract surgery
For cataract surgery in children, the latest ultrasound platform Alcon Infinity is used.
Synoptophore
Instrument for diagnosing and treating imbalance of eye muscles.
Maddox cross and prisms
Diagnostic equipment for measuring the amount of deviation angle and preoperative calculation in strabismus surgery